Authorisation within AFS
How to authorize access to directories and files.
Access control in AFS is done via ACLs (Access Control List). You can
give different rights to multiple AFS-users and AFS-groups.
In this respect the access control is more fine-grained than normal
Unix-rights.
However, access rights in AFS are based on directories. That means if
you have access to one file in a directory, you have access to all of
them.
ACLs for new directories are inherited from the parent directory.
The rights one can give/have are explained in the AFS-Glossary.
UNIX
Using access rights
You can list the access rights for a directory in unix with the command “fs listacl <path>”.
e.g.
# fs listacl /afs/ipp-garching.mpg.de/
Access list for /afs/ipp-garching.mpg.de/ is
Normal rights:
system:administrators rlidwka
system:anyuser rl
afsbackup rl
! You can get more detailed information on the man-page on the
login-node rzgate “man fs_listacl”. Just make sure the path
“/afs/ipp-garching.mpg.de/common/man” is in your MANPATH-environment
variable.
Similarly, you can set the access rights for a directory in unix
with the command “fs setacl <path> (user|group) rights”.
The details are given again on the man-page : “man fs_listacl”.
Unfortunately, there is no recursive version of the fs setacl command.
However, you can set ACLs recursively by using the (GNU!) “find”
command :
find <path> -noleaf -type d -exec fs setacl "{}" (user|group) <rights> \;
! Is should be noted, that access rights are inherited when creating a new directory.
! Best Practices :
When setting up a shared directory for a project, you should really create a group. With groups it is much easier to give rights to new members of the project.
Usually, 2 groups are better: <Project>-readers and <Project>-Writers.
AFS-groups
Each AFS-user can create up to 20 groups for her personal use, which is encouraged when sharing directories with more than 2 persons.
The relevant commands are :
pts creategroup : create a new group (man pts_creategroup)
pts delete : delete a group (use with care!) (man pts_delete)
pts listowned : show your groups (man pts_listowned)
pts membership : show the members of a group – or – the groups a user is member of. (man pts_membership)
pts removeuser : remove a user from a group (man pts_removeuser)
In case you wonder, there are some global groups:
system:administrators : admins of this cell
system:authuser : people with a valid token for this AFS-cell.
system:anyuser : Anyone in the world with an AFS-client
You should be careful when giving rights to any of those groups.
Windows
In windows you may see AFS-information and manipulate access rights through the Explorer-extension.
For this, you just right-click on a directory in the explorer:
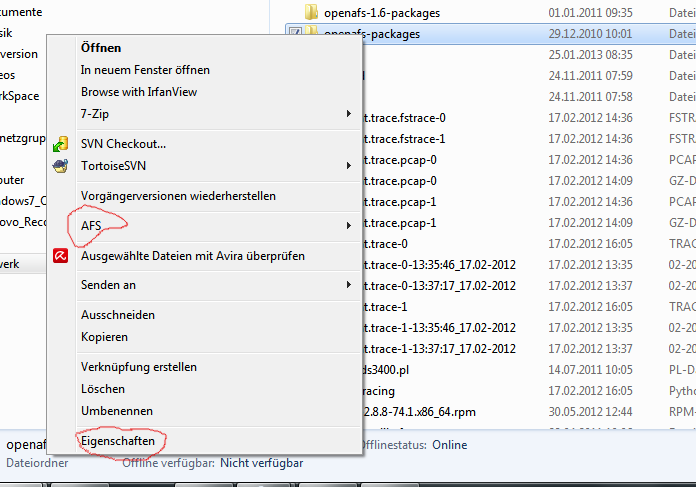
You can then see AFS-information either through the AFS-submenu or the properties (here: “ Eigenschaften”) menu.
In these submenus you can also modify the ACLs on an AFS-directory
Powershell
You can also use the powershell to change the ACLs via a script.
The relevant commands are called “pts.exe” and “fs.exe”. The usage is as described above.
If you want to change a directory-hierarchy recursively, in the powershell do a :
gci <PATH> -Recurse -Directory | Foreach { fs.exe setacl "$_.fullname" <user|group> <rights> }
Here you need to substitute:
<PATH> is a UNC path like \\AFS\ipp-garching.mpg.de\…
<user|group> the AFS-user or group
<rights> the AFS-rights as explained in the AFS-Glossary.
NOTE
When adding/removing a user to a group, it may take up to 2 hours until
it takes effect.
The user added/removed to the group can speed up this process by
discarding the old token and obtaining a new one.