AFS Basics
Understanding AFS
Some general information regarding AFS.
Separation of data and metadata
In AFS, the information where the data are stored is stored on different
servers than the data itself.
The servers storing the data are called fileserver. The servers storing
the information are called volume-location-server (database-server).
A client connects to AFS for the first time after a reboot
When a client wants to find a file in an afs-cell it has not connected before, it first asks the database-server, which fileserver serves the volume it is asking for. Then it goes to that server and tries to retrieve the data.
Required Firewall rules
In order for AFS to work correctly, you must allow connections from outside on the UDP port 7001 coming from the UDP ports 7000-7012.
Structure of the /afs - filesystem
On the highest level, AFS is split into Cells. An AFS-cell is an administrative unit.
The MPCDF administers the cell “ipp-garching.mpg.de” and e.g. CERN’s cell is reachable under /afs/cern.ch/.
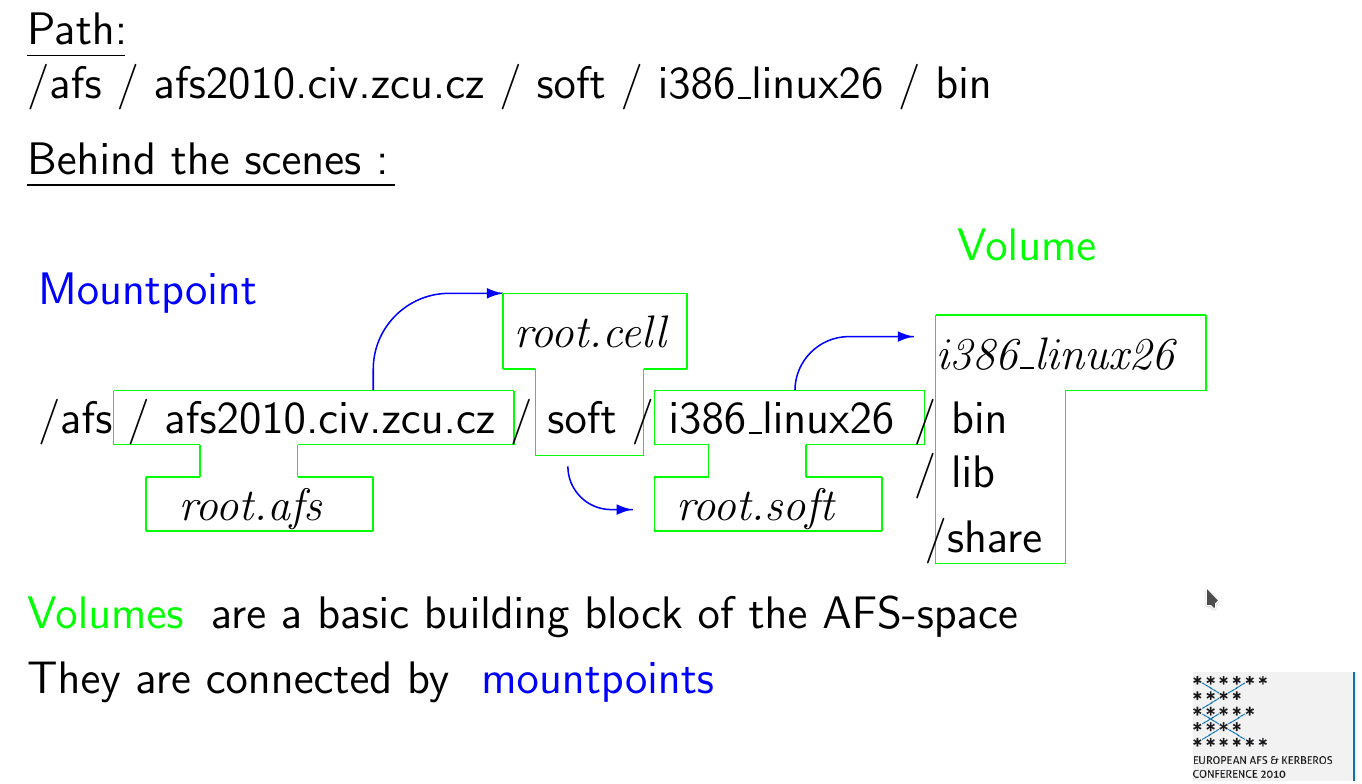
Within one AFS-Cell, the filesystem itself is build out of volumes, which are connected by mountpoints.
Volumes are comparable to disc-partitions with a few extension :
A volume may be moved from one disc to another or even from one server to another.
A volume may have a read-only (RO) snapshot spread on different servers.
Thus, /afs/ipp-garching.mpg.de is a mountpoint to the volume “root.cell” within the AFS-cell “ipp-garching.mpg.de”
See a simple diagram (taken from a talk) about the structure
Security within AFS
Authentication (who are you ?)
To prove AFS-Servers who you are you need to present an AFS-token,
which can be derived from a Kerberos-Ticket.
Read more about this
here.
Authorisation (what are you allowed to do ?)
The access rights to a directory in AFS are controlled by so-called
Access Control Lists (ACLs).
Read more about them
here.
Further documentation:
Manpages are installed under /afs/ipp-garching.mpg.de/common/man/.
When your MANPATH environment variable is containing that path (like it
should, e.g. on the MPCDF login node), then you can use those for most
AFS-Commands.
Modern linux distributions also ship the man-pages with the client packages.
Also consider the official documentation at openafs.org.